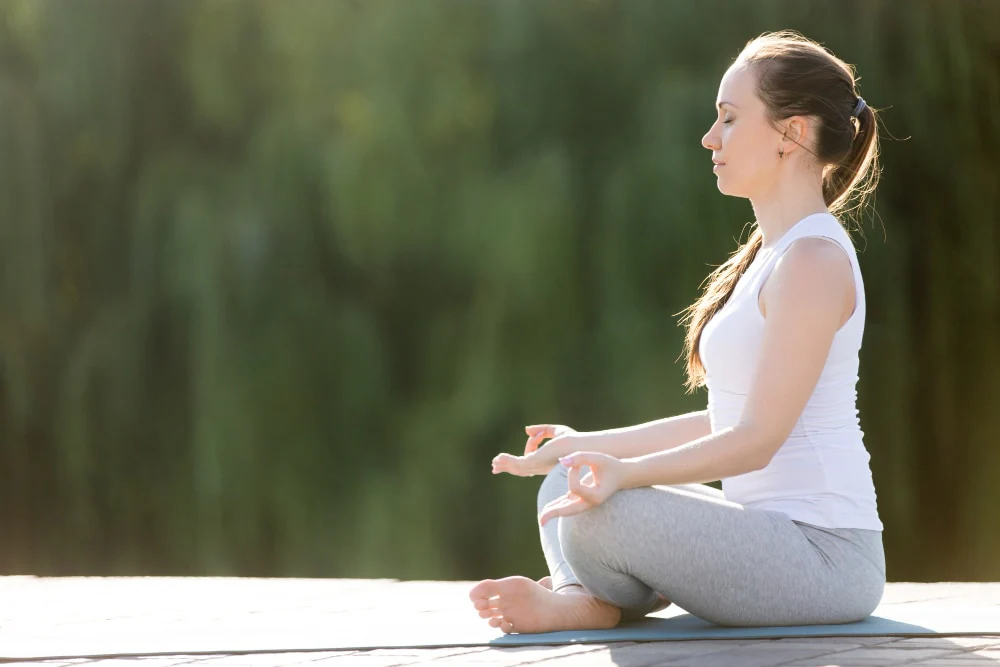
Quality sleep is crucial for our general health, but many find it challenging to attain. Stress, anxiety, and daily responsibilities can affect our ability to sleep well. Adding certain breathing exercises to your nightly routine can enhance your sleep through mental and physical relaxation. These exercises are simple, efficient, and can be performed at home.
This article explores 10 breathing techniques designed to improve your sleep and provide a more restful night.
1. 4-7-8 Breathing
The 4-7-8 breathing technique is a straightforward yet effective way to alleviate stress and induce relaxation. It involves inhaling through the nostril for four counts, retaining the breath for seven repetitions, and releasing through the mouth for eight consecutive counts.
This sequence helps lower the heart rate and promote bodily relaxation, facilitating an easier transition into sleep. The structured rhythm of the breaths assists in calming the mind and priming the body for rest, thereby improving overall sleep quality.
2. Diaphragmatic Breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, prioritizes the deep inhalation of the diaphragm over shallow respiration from the chest. To practice this technique, take a comfortable position on the floor, put one hand on your chest and another on your tummy, and take a deep breath.
Ensure that your chest remains stationary while your abdomen rises. This approach enhances oxygen intake and fosters a sense of tranquility, effectively enhancing sleep quality by minimizing stress and promoting relaxation.
3. Box Breathing
Box breathing is a widely adopted method for stress management and improving focus. In this method, the individual inhales for four seconds, holds their breath for a further four seconds, exhales for four seconds, and then holds their breath for an additional four seconds.
This structured breathing pattern effectively reduces anxiety and cultivates a serene state, making it particularly beneficial as a pre-sleep practice. By focusing on the rhythm of your breathing, box breathing can help quiet the mind and prepare the body for a restful night.
4. Alternate Nostril Breathing
Alternate nostril breathing is an ancient technique for coordinating the mind and body. This practice entails closing one nostril with a finger, inhaling through the other nostril, and then switching sides to exhale. This rhythmic pattern is repeated, alternating between nostrils.
By facilitating a balanced airflow through the nasal passages, this method can alleviate stress and promote relaxation. Incorporating alternate nostril breathing before bedtime can aid in clearing the mind and readying the body for sleep, thereby enhancing overall sleep quality.
5. Progressive Relaxation Breathing
Progressive relaxation breathing integrates deep breathing with muscle relaxation to relieve physical tension and stress. Begin by inhaling deeply and tensing a specific muscle group for approximately five seconds. Upon exhaling, consciously release the tension in that muscle group. Repeat this process with various muscle groups across the body.
Progressive relaxation breathing promotes mental and bodily calmness by systematically releasing physical tension. This facilitates easier sleep onset and a more profound, rejuvenating sleep experience.
6. Guided Visualization Breathing
Guided visualization breathing combines deep breathing with mental imagery to foster relaxation. Locate a peaceful place, shut your eyes, and inhale steadily and thoroughly. While doing so, envision a serene scene like a beach or forest, immersing yourself mentally in that environment.
This practice helps to divert attention from daily pressures and induce a feeling of peace. Guided visualization breathing is an effective way to ready the mind and body for sleep, ultimately enhancing sleep quality.
7. Mindful Breathing
Mindful breathing involves directing awareness to the breath and the present instant. To engage in mindful breathing, settle into a comfy place, shut your eyes, and breathe inherently. Concentrate on how you feel about every breath entering and departing your body.
If you find it challenging to maintain focus, we suggest using a breathing exercise device. This can effectively relieve stress and anxiety by bringing you back to the present moment, facilitating easier sleep initiation and maintenance.
8. Resonant Breathing
Resonant breathing involves taking deep, slow breaths consistently to help regulate the autonomic nervous system. To accomplish this, it is necessary to inhale for five counts and out five times. This slow and steady breathing pattern can help synchronize your heart rate and promote a state of relaxation.
Practicing resonant breathing before bed can help calm the nervous system and prepare the body for rest, improving overall sleep quality.
9. Buteyko Breathing
Buteyko breathing is designed to decrease hyperventilation and enhance breathing efficiency. This technique involves taking small, gentle inhalations through the nose, followed by a small exhalation, and briefly holding the breath.
The goal is to stabilize breathing patterns and alleviate stress. By encouraging efficient breathing, Buteyko breathing can promote relaxation of the mind and body, facilitating easier sleep onset and improving overall sleep quality.
10. Pursed Lip Breathing
Pursed lip breathing is a technique where you inhale through your nose for two counts and exhale through pursed lips for four counts. This method regulates the breathing pace and enhances oxygen intake into the lungs.
It is especially advantageous for those with respiratory disorders, as it enhances circulation. Practicing pursed lip breathing before bedtime encourages relaxation, relieves anxiety, and helps achieve cozy sleep.
Conclusion
Integrating these breathing exercises into your nightly regimen may significantly enhance the quality of your sleeping experience. Each technique fosters relaxation and diminishes stress, establishing an ideal setting for restful sleep. Consistent practice of these methods can enhance overall sleep wellness, ensuring a more revitalizing night’s rest.