Tooth infections, medically referred to as dental abscesses, develop when bacteria infiltrate the dental pulp—the innermost part of the tooth that houses blood vessels and nerves—or the surrounding tissues. These infections, if diagnosed and treated early, can usually be managed effectively. However, when neglected, they can escalate into severe, potentially fatal complications. It is vital to understand how tooth infections progress and the serious health risks they pose to ensure timely and appropriate treatment and prevention.
Causes Of Tooth Infections

- Dental Caries (Cavities)
- Bacteria break down the enamel and dentin of a tooth.
- This erosion allows bacteria to reach the pulp, leading to infection.
- Gum Disease
- advanced stages of periodontal disease create pockets around the teeth.
- These pockets become breeding grounds for bacteria, causing infection.
- Trauma
- Cracks or breaks in a tooth can provide an entry point for bacteria.
- The bacteria can then invade the dental pulp and cause infection.
- Failed Dental Work
- Improper dental procedures can leave areas vulnerable to bacterial invasion.
- Unaddressed complications from previous dental treatments can also lead to infections.
Symptoms Of A Tooth Infection
The symptoms of a tooth infection can vary, but they generally include:
- Severe Toothache
- Intense, persistent pain in the affected tooth.
- Pain can radiate to the jaw, ear, or neck.
- Sensitivity to Hot and Cold
- Heightened sensitivity when consuming hot or cold foods and drinks.
- Discomfort may persist even after the stimulus is removed.
- Swelling in the Gums or Face
- Noticeable swelling around the infected tooth.
- Swelling can extend to the face, jaw, or neck.
- Fever
- Elevated body temperature as the body fights the infection.
- Fever may be accompanied by chills or sweating.
- Bad Breath or a Foul Taste in the Mouth
- Persistent bad breath that does not improve with oral hygiene.
- A foul taste due to pus drainage from the infection site.
- Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing (in Severe Cases)
- Swelling and infection spreading to the throat or airways.
- This can cause significant discomfort and requires immediate medical attention.
Progression Of A Tooth Infection
The progression of a tooth infection can be categorized into different stages:
Early Stage
- Localized Pain and Swelling
- The infection initially causes pain and swelling around the affected tooth.
- At this stage, the infection is confined to the dental pulp.
Intermediate Stage
- Spreading Infection
- If untreated, the infection spreads to surrounding tissues.
- This leads to the formation of a dental abscess, characterized by significant swelling, pain, and pus.
- Systemic Symptoms
- As the infection progresses, systemic symptoms may develop.
- These can include fever, general malaise, and enlargement of lymph nodes.
Advanced Stage
- Spread to Facial Spaces
- The infection can extend to the facial spaces, resulting in cellulitis.
- Cellulitis is a serious bacterial skin infection that requires immediate attention.
- Osteomyelitis
- The infection can reach the jawbone, leading to osteomyelitis.
- Osteomyelitis is a severe bone infection that can cause significant health issues.
- Sepsis
- If bacteria enter the bloodstream, sepsis can occur.
- Sepsis is a life-threatening condition marked by a systemic inflammatory response and potential organ failure.
Can A Tooth Abscess Kill You?
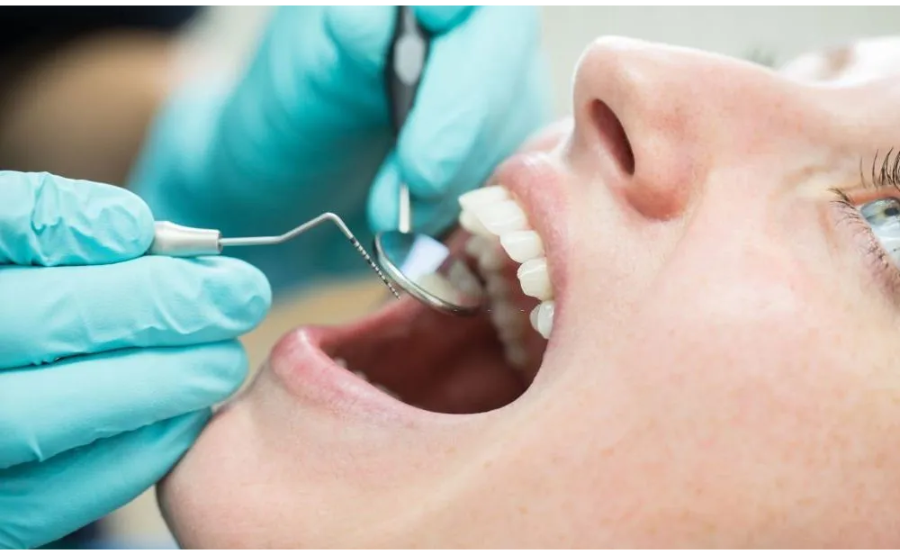
A tooth infection occurs when oral bacteria invade the core of the tooth, leading to the formation of pus within the soft tissues. This condition is frequently associated with tooth decay but can also result from chipped or damaged teeth. When the protective enamel is compromised, bacteria find a conducive environment to grow and spread to nearby teeth, tissues, and roots.
If the infection is treated promptly, it can be managed effectively, resulting in healthy teeth and gums. However, if left untreated, the infection worsens over time. The bacteria can gradually spread to other parts of the body, overwhelming the body’s immune system. This can lead to a situation where the immune system is no longer able to contain the infection, resulting in severe health complications.
When Does A Tooth Infection Become Life-Threatening?
A tooth infection can sometimes occur following dental surgery. While antibiotics prescribed by your dentist are typically effective at controlling the infection, untreated tooth infections can lead to serious complications, including:
- Sepsis
- A severe, life-threatening reaction occurs when the body responds to an infection with widespread inflammation.
- Symptoms include high fever, dizziness, shortness of breath, and digestive issues.
- Necrotizing Fasciitis
- A severe infection that causes the rapid inflammation and death of soft body tissues.
- This condition can be fatal if not treated promptly.
- Ludwig’s Angina
- A serious bacterial infection that affects the floor of the mouth, underneath the tongue, and surrounding tissues.
- This can lead to airway obstruction and requires immediate medical attention.
- Blood Clots
- Tooth infections can lead to the formation of blood clots, particularly in the sinuses.
- Clots near the brain can result in severe complications and pose a significant health risk.
- Mediastinitis
- A severe condition characterized by inflammation between the lungs.
- This condition is potentially fatal and requires urgent treatment.
- Osteomyelitis
- The infection can spread to the bones, leading to osteomyelitis, a serious and life-threatening bone infection.
Additionally, untreated tooth infections can cause
- Endocarditis
- An infection of the heart valves, which can be life-threatening and demands immediate medical intervention.
- Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
- A rare but serious condition where a blood clot forms in the cavernous sinus, a large vein at the base of the brain.
- Brain Abscess
- Bacteria from a tooth infection can spread to the brain, causing a brain abscess.
- Symptoms include severe headaches, neurological deficits, and altered mental status.
These complications underscore the importance of timely and professional treatment of tooth infections to prevent them from becoming life-threatening.
4 Risk Factors Associated With Tooth Infection

Certain individuals are more susceptible to developing severe complications from tooth infections due to various risk factors
- Older Age
- Adults of advanced age are at a heightened risk of developing tooth infections that can lead to severe conditions.
- Aging can weaken the immune system and increase susceptibility to infections, making older adults more prone to medical complications.
- Immunity
Immunocompromised individuals, such as those with weakened immune systems due to medical conditions or medications, are more vulnerable.
- Their bodies may struggle to mount an effective defense against infections, prolonging the duration of illness and increasing the risk of complications.
- Diabetes
- People with diabetes face an elevated risk of health complications, including those related to tooth infections.
- Impaired metabolism and insufficient insulin production can compromise the body’s ability to combat infections effectively.
- Malnourishment
- Individuals suffering from malnourishment, either due to chronic illness or past health issues, are more susceptible to infections.
- Malnourishment weakens the body’s overall resilience and ability to fight off infections, making it harder to combat dental infections effectively.
These risk factors highlight the importance of proactive dental care and prompt treatment of tooth infections, particularly in individuals with underlying health conditions or compromised immune systems. Early intervention can help mitigate the risk of severe complications and promote better oral and overall health.
Complications Of An Untreated Tooth Infection
Here are some severe complications that can arise from untreated tooth infections:
- Ludwig’s Angina: This is a fast-progressing cellulitis that affects the floor of the mouth. It can obstruct the airway, causing breathing difficulties.
- Mediastinitis: Infection can spread to the mediastinum, the central compartment of the thoracic cavity, causing severe chest pain and systemic illness.
- Brain Abscess: Bacteria from a tooth infection can spread to the brain, resulting in a brain abscess. Symptoms include severe headaches, neurological deficits, and altered mental status.
- Endocarditis: Bacteria can infect the heart valves, leading to endocarditis, a life-threatening condition that demands immediate medical attention.
Treatment And Prevention
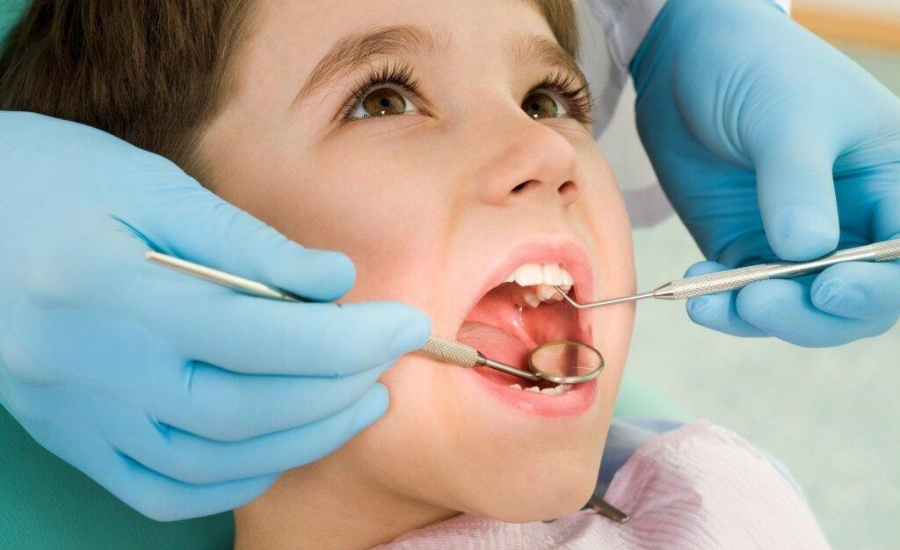
Immediate Treatment
- Antibiotics: These are prescribed to control the bacterial infection and prevent its further spread.
- Drainage: In some cases, surgical drainage of the abscess may be necessary to remove pus buildup and alleviate symptoms.
- Root Canal Therapy: This procedure involves removing the infected pulp from the tooth’s interior to save the tooth and prevent further infection.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases where the tooth cannot be saved, extraction may be necessary to prevent the infection from spreading.
Preventive Measures
- Regular Dental Checkups: Routine dental visits are crucial for identifying and addressing dental issues early, before they progress into infections.
- Good Oral Hygiene: Maintaining proper oral hygiene practices, such as brushing teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash, helps remove bacteria and prevent cavities.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet low in sugar reduces the risk of cavities and helps maintain overall oral health.
- Prompt Treatment: Addressing dental pain and swelling immediately is essential to prevent the progression of infections and avoid complications.
How Do You Know If A Tooth Infection Has Spread To Your Blood?
Sepsis is a serious medical condition that occurs when an infection spreads from its original site to the bloodstream. While the risk of sepsis from a tooth infection in the early stages is relatively low, it can quickly become life-threatening if left untreated.
This condition poses severe complications as bacteria travel to other organs and body systems, leading to systemic inflammation and dysfunction. Signs and symptoms of sepsis, such as fever, soreness, and high fever, may manifest as the infection spreads to the blood.
Immediate medical attention is crucial if you experience these symptoms, especially in the context of a tooth infection. Understanding the signs of sepsis and seeking prompt treatment can help manage the condition effectively and prevent potentially fatal outcomes.
Can Antibiotics Cure A Tooth Infection?
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed for the treatment of dental infections, but it’s essential to understand their role and limitations:
- Control of Infection Spread: Antibiotics play a vital role in controlling the spread of existing infections by targeting and eliminating bacteria from the affected area.
- Supplementary Treatment: However, antibiotics alone are not typically sufficient to fully address dental abscesses. They are often used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that may include other therapies.
- Addressing Root Cause: To effectively treat the infection, it’s crucial to address the root cause, which is usually an infected tooth or gum disease. Procedures like root canal therapy, periodontal treatment, or tooth extraction may be necessary to fully eradicate the infection.
- Risk of Antibiotic Resistance: Over-reliance or misuse of antibiotics can contribute to antibiotic resistance, a significant global health concern where bacteria become less responsive to these drugs.
- Temporary Symptom Management: While antibiotics can help manage symptoms temporarily, they do not eliminate the underlying cause of the infection. Therefore, it’s essential to follow up with a dentist to ensure proper treatment of the infection’s source and prevent potential complications from recurring.
FAQs
1. What causes a tooth infection?
Tooth infections are primarily caused by:
- Dental Caries (Cavities): Bacteria break down the enamel and dentin, reaching the pulp.
- Gum Disease: Advanced periodontal disease can cause pockets of infection around the teeth.
- Trauma: Cracks or breaks in the teeth can allow bacteria to enter the pulp.
- Failed Dental Work: Improper dental procedures or unaddressed complications can lead to infections.
2. What are the common symptoms of a tooth infection?
The symptoms of a tooth infection generally include:
- Severe toothache
- Sensitivity to hot and cold
- Swelling in the gums or face
- Fever
- Bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing (in severe cases)
3. How does a tooth infection progress if left untreated?
- Early Stage: Localized pain and swelling around the affected tooth.
- Intermediate Stage: Spreading infection causing a dental abscess, systemic symptoms like fever and malaise.
- Advanced Stage: Spread to facial spaces, osteomyelitis (jawbone infection), and sepsis (life-threatening systemic infection).
4. What are the risk factors for severe complications from a tooth infection?
- Older Age: Higher risk of severe complications.
- Immunity: Immunocompromised patients have a slower response to infections.
- Diabetes: Impaired metabolism and lack of insulin increase the risk of complications.
- Malnourishment: Chronic disease or past illnesses can make it harder for the body to fight infections.
5. How can a tooth infection become life-threatening?
A tooth infection can lead to life-threatening conditions such as:
- Sepsis: Severe systemic response to infection.
- Ludwig’s Angina: Rapidly progressing cellulitis of the mouth floor.
- Necrotizing Fasciitis: Severe infection leading to tissue death.
- Mediastinitis: Inflammation in the central thoracic cavity.
- Osteomyelitis: Severe bone infection.
6. Can antibiotics cure a tooth infection?
Antibiotics can help control the spread of an existing infection and assist the body in eliminating bacteria. However, antibiotics alone are not the definitive treatment. They are used alongside other treatments like drainage, root canal therapy, or tooth extraction to fully address the infection’s source.
7. What are the signs that a tooth infection has spread to the bloodstream?
Signs of sepsis from a tooth infection include:
- High fever
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Digestive issues
- Soreness and general malaise
8. How can you prevent tooth infections?
Preventive measures include:
- Regular dental checkups to identify and treat dental issues early.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing twice a day, flossing, and using mouthwash.
- Following a healthy diet and reducing sugar intake.
- Promptly addressing dental pain and swelling with professional help.
Conclusion
If a tooth infection is not treated promptly, it can quickly escalate from a minor dental problem to a life-threatening situation within days or weeks. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the risk factors, and being aware of the progression stages are crucial for receiving timely treatment.
While antibiotics are important for controlling bacterial infections, they should be part of a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses the underlying cause of the infection. Regular dental check-ups, maintaining good oral hygiene practices, and seeking immediate professional help for any dental issues are essential for preventing serious complications and maintaining overall health. If you notice any signs of a tooth infection, it’s important to seek dental care promptly to reduce the risk of severe complications or even death.
Keep in touch for ongoing updates and notifications. Vents Breaking!